Spinal chord
The Spinal chord is the long cylindrical lower part of central nervous system . It occupies upper (2/3) two-third of vertebral canal. And is enclosed in the three meninges.
It gives rise to 31 pairs of spinal nerves and retains the basic structural pattern.
Features :
- The Spinal chord is 18 inches or 45 cm in male and 42 inches in female .
- it extend from the upper border of the atlas vertebra to the lower border of first lumbar vertebra. In childrane it extents up to the L3 vertebra.
- Superiorly , it is continuous with medula oblengeta.
- inferiorly it terminates as conus medullaries .
- As the Spinal chord is much shorter than the length of the vertebral column.
Meningeal covering :
- The spinal chord is surrounded by the three meninges.
- The outer is the Dura mater .
- Middle is Arachnoid mater.
- Inner most is Pia mater.
- The space between the dura mater and arachnoid mater is called Subdural space
- The arachnoid and pia mater is seperated by subarachnoid space which contain cerebrospinal fluid.
External structure of spinal chord :
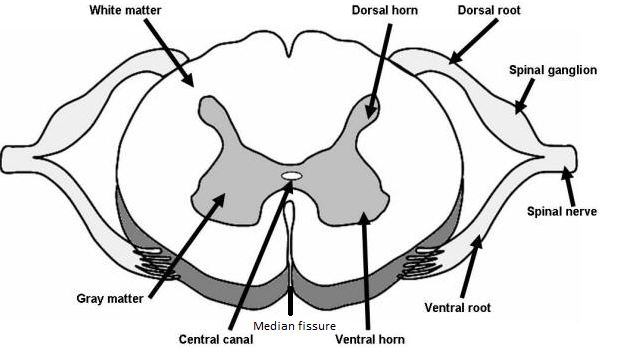
- Anteriorly, the spinal chord reveal a deep anterior median fissure lodging the anterior spinal artery.
- posterior median sulcus is a thin thin longitudinal groove from which a septum runs in the depth of spinal chord.
- Each half is subdivided into anterior , lateral and posterior regions by by anterolateral and posterolateral sulci .
- Ventral or motar nerves roots emerge from the anterolateral sulcus.
- Dorsal or sensory nerve roots enter spinal cord from poserolateral sulcus.
Internal Structure :
- White matter, i.e. nerve fibers lie outside and gray matter lies inside. In the center of gray matter is the central canal containing CSF.
- The gray matter is in the form of "H" with ray commissure joning the gray matter of right and left sides.
- The gray matter comaprises one posterior horn and the oe anterior horn on each side in the entire extent of the cord.
- Shape and size of horn is differ in different segments due to functional reasons
Function :
- The spinal cord functions primarily in the transmission of nerve signals from the motor cortex to the body, and from the afferent fibers of the sensory neurons to the sensory cortex.
- It is also a center for coordinating many reflexes and contains reflex arcs that can independently control reflexes.
Clinical anatomy :
- Conus medullaris syndrome : Due to injury to S2,S3,S4 segment of spinal chord . Fatures are : a. Anaesthesia inthe perinium. The region is supplied by the three segments. b. Sexual functions aremaffected as same nerves carry out sexual functions.
- Spinal tumours can occur in the spinal cord and these can be either inside (intradural) or outside (extradural) the dura mater.
- Spinal cord injuries can be caused by trauma to the spinal column (stretching, bruising, applying pressure, severing, laceration, etc.). The vertebral bones or intervertebral disks can shatter, causing the spinal cord to be punctured by a sharp fragment of bone.
- In milder cases, a victim might only suffer loss of hand or foot function.
More severe injuries may result in paraplegia, tetraplegia (also known as quadriplegia), or full body paralysis below the site of injury to the spinal cord.








No comments:
Post a Comment