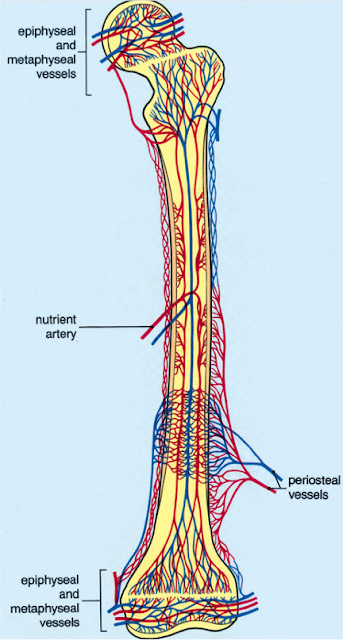
Blood supply of long bone
- Blood supply of long bone accounts for 5 to 10 % of the cardiac output.
- Long bone receives blood supply from various sources-
- Nutrient arteries
- Epiphyseal arteries
- Metaphyseal arteries
- Periosteal arteries.
Arterial Supply
- Nutrient artery :
- One or two diaphyseal nutrient arteries enter the shaft through nutrient foramina.
- In the medullary cavity, the nutrient arteries divide into ascending and descending branches.
- Each branch divides into number of small parallel channels, after reaching the epiphysis they divide repeatedly into small rami which pursue spiral courses.
- Near the epiphysis, they are joined by metaphyseal and epiphyseal arteries.
- Primary direction of the blood flow is centrifugal.
2. Epiphyseal arteries :
- When articular cartilage and epiphyseal cartilage are continuous, the epiphyseal arteries pierce the epiphyseal cartilage and supply the epiphysis.
- If these arteries are damaged in epiphyseal separation, avascular necrosis of epiphysis may occur, e.g. head of the femur.
- In others, where the articular cartilage is not continuous with epiphyseal cartilage, the epiphyseal arteries enter the epiphysis without piercing it.
- In these cases, epiphyseal separation will not cause avascular necrosis.
- Epiphyseal arteries are derived from the periarticular vascular arcades.
- Out of many vascular foramina near epiphysis, very few admit arteries and rest are venous exits.
- Epiphyseal arteries anastomose with metaphyseal and nutrient arteries after fusion of diaphysis and epiphysis.
3. Metaphyseal arteries :
- Numerous small blood vessels arising from the anastomosis around the joint pierce the metaphysis along the attachment of the joint capsule.
- Metaphyseal arteries freely anastomose with spiral branches of nutrient arteries, so metaphysis is the most vascular area of the long bone.
4. Periosteal arteries :
- Many blood vessels anastomose beneath the periosteum and enter the Volkmann’s canal and supply the outer third of the compact bone.
- Periosteal arteries penetrate bone at these sites where fascial sheath or aponeurosis gain attachment to the shaft.
 |
| Long bone blood supply |
Venous Drainage :
Valveless nutrient veins accompany the arteries.
· In medullary cavity, a central venous sinus is present which is served by radial collecting sinuses.
· The general layout is fan-shaped with cortical sinusoids radiating outwards towards periosteal surface.
· Each haversian canal is supplied by a solitary sinusoid.







No comments:
Post a Comment