Brachial Plexus
- The brachial plexus is a network (plexus) of nerves (formed by the anterior rami of the lower four cervical nerves and first thoracic nerve (C5, C6, C7, C8, and T1).
- This plexus extends from the spinal cord, through the cervicoaxillary canal in the neck, over the first rib, and into the armpit. It supplies afferent and efferent nerve fibers to the chest, shoulder, arm, forearm, and hand.
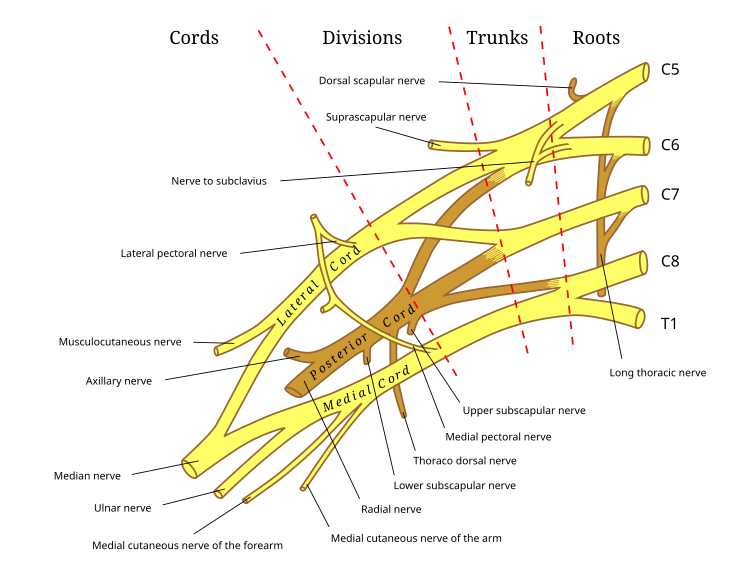
- The brachial plexus is divided into five roots, three trunks, six divisions (three anterior and three posterior), three cords, and five branches.
Roots : The roots are the five anterior primary rami of the spinal nerves, after they have given off their segmental supply to the muscles of the neck.
The brachial plexus emerges at five different levels;
- C5 (C5 and C6 merge to establish the upper trunk,)
- C6 ( C5 and C6 merge to establish the upper trunk,)
- CC7 (C7 continuously forms the middle trunk)
- C8 (C8 and T1 merge to establish the lower trunk)
- T1 (C8 and T1 merge to establish the lower trunk)
Trunks : These roots merge to form the Trunks
Divisions : Each trunk then splits in two, to form six Divisions : i.e. anterior, posterior.
- anterior divisions of the upper, middle, and lower trunks.
- posterior divisions of the upper, middle, and lower trunks.
Cords : These six divisions regroup to become the three Cords . The cords are named by their position with respect to the axillary artery.
- The posterior cord is formed from the three posterior divisions of the trunks (C5-C8, T1)
- The lateral cord is formed from the anterior divisions of the upper and middle trunks (C5-C7)
- The medial cord is simply a continuation of the anterior division of the lower trunk (C8, T1)
Clinical Anatomy :
- The injuries to different part of brachial plexus may leads to characteristic clinical features.
- Injury to the brachial plexus may affect sensation or movement of different parts of the arm.
- Injury can be caused by the shoulder being pushed down and the head being pulled up, which stretches or tears the nerves.
- For the upper brachial plexus injuries, paralysis occurs in those muscles supplied by C5 and C6 like the deltoid, biceps, brachialis, and brachioradialis.
Injuries during birth : Brachial plexus injuries can occur during the delivery of newborns when after the delivery of the head, the anterior shoulder of the infant cannot pass below the pubic symphysis without manipulation. This manipulation can cause the baby's shoulder to stretch, which can damage the brachial plexus to varying degrees.
- Erb's point The nerve point of the neck, also known as Erb's point[1] is a site at the upper trunk of the brachial plexus located 2–3 cm above the clavicle.
- Injury to Erb's point is commonly sustained at birth or from a fall onto the shoulder. The nerve roots normally involved are C5 and partly C6.







No comments:
Post a Comment