Structure of Ear :
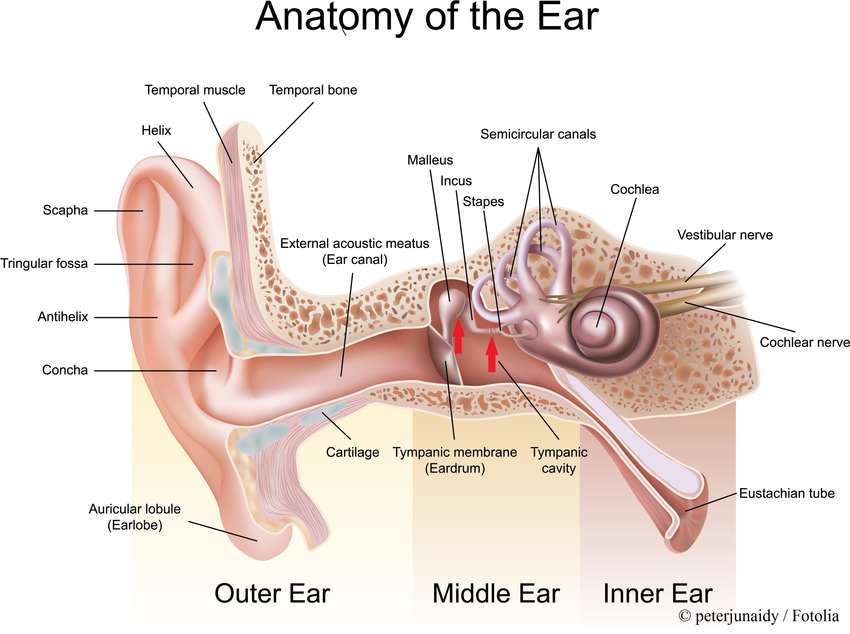
Outer Ear :
- The outer ear is the external portion of the ear and includes the fleshy visible pinna (also called the auricle), the ear canal, and the outer layer of the eardrum (also called the tympanic membrane).
- Pinna : The flap like structure on either side of head is the Pinna. It is made up of elastic fibrocartilage covered by skin that is why it is very flexible. Soft lower projecting part is the lobule of the ear .
- External auditory meatus. (ear canal) : From the external opening on the lateral side of the head to the tympanic memebrane (ear drum ) extents as a "S" shaped tube known as the external meatus. It is about 26 mm long and 7 mm in diameter . It is lateral 1/3rdb is cartilaginous and medial 2/3rd is bony. The external auditory meatus is internally lined by the skin having numerous ceruminous glands. ( wax producing glands ) and hair.

- Tympanic membrane : Tympanic membrane seprates the external ear from the middle ear. The surface of tympanic membrane towards the external auditory meatus is lined by the skin . The surface of the tympanic membrane towards the middle ear is lined by the mucous membrane . In between the two layer is a fibrous tissue. Malleus and incus are releted here on the medial side of tympanic membrane.
Middle Ear ( Tympanic cavity ) :
- The middle ear lies between the outer ear and the inner ear.
- It consists of an air-filled cavity called the tympanic cavity and includes the three ossicles and their attaching ligaments; the auditory tube; and the round and oval windows.
- The middle ear also connects to the upper throat at the nasopharynx via the pharyngeal opening of the Eustachian tube.
- It is dumbbell shaped air filled cavity in the petrous part of temporal bone .
- It has roof, a floor, an anterior wall , a posterior wall ,a medial wall , and lateral wall.
- Roof : Pectorus part of temporal bone
- Floor : Petrous part of temporal bone.
- Anterior wall : Petrous part of temporal bone in which opens the auditory tube . this tube maintaining same air pressure on both the sides of tympanic membrane .
- Posterior Wall : Air filled cavity in the pectrous part of temporal bone known as the mastoid antrum .
- Lateral wall : Tympanic membrane is present on that side.

- Midde ear is linned by the mucous membrane and three small bones i.e. malleus , incus , stapes .
- The ossicles are three small bones that function together to receive, amplify, and transmit the sound from the eardrum to the inner ear.
- The ossicles are the malleus (hammer), incus (anvil), and the stapes (stirrup).
- The stapes is the smallest named bone in the body.
- The three ossicles transmit sound from the outer ear to the inner ear. The malleus receives vibrations from sound pressure on the eardrum, where it is connected at its longest part (the manubrium or handle) by a ligament. It transmits vibrations to the incus, which in turn transmits the vibrations to the small stapes bone. The wide base of the stapes rests on the oval window. As the stapes vibrates, vibrations are transmitted through the oval window, causing movement of fluid within the cochlea.
Inner Ear :
- The inner ear sits within the temporal bone in a complex cavity called the bony labyrinth.
- A central area known as the vestibule contains two small fluid-filled recesses, the utricle and saccule.
- There is a bony labyrinth inside which is membranous labyrinth . It lies in the pectoral part of the temporal bone .
- The membranous labyrinth is filled with the fluid called endolymph.

- Bony labyrinth consist of three parts,
- Cochlea ( Anteriorly )
- Vestibule (Middle )
- Semicircular canal ( Posteriorly ) .
- Membranous labyrinth : It lies within bony labyrinth separated by watery fluid known as perilymph. inside the membranous labyrinth is watery fluid known as endolymph . Vibrations are transmitted into the inner ear into a fluid called endolymph, which fills the membranous labyrinth.
Functions :
Hearing : Sound waves travel through the outer ear, are modulated by the middle ear, and are transmitted to the vestibulocochlear nerve in the inner ear. This nerve transmits information to the temporal lobe of the brain, where it is registered as sound.
Balance : Providing balance, when moving or stationary, is also a central function of the ear. The ear facilitates two types of balance: static balance, which allows a person to feel the effects of gravity, and dynamic balance, which allows a person to sense acceleration.







No comments:
Post a Comment